Factors Influencing Block Count

The number of blocks needed to construct a 2-bedroom flat is influenced by various factors, including the size of the flat, the building materials used, and local building codes.
Flat Size and Block Count
The size of the flat directly impacts the number of blocks required. Larger flats naturally require more blocks to accommodate the increased floor area. Here’s a breakdown of average block counts for different flat sizes:
- 600 sq ft: Approximately 1,000-1,200 blocks
- 800 sq ft: Approximately 1,300-1,500 blocks
- 1,000 sq ft: Approximately 1,600-1,800 blocks
These are estimates and can vary based on factors like wall thickness, ceiling height, and the design of the flat.
Building Material Impact
The type of building material used significantly influences the block count. Different materials have varying strengths and densities, impacting the number of blocks needed for structural integrity.
- Concrete blocks: Concrete blocks are known for their strength and durability, requiring fewer blocks for construction compared to other materials.
- Brick blocks: Brick blocks are generally lighter than concrete blocks, requiring a higher number for construction.
- Timber blocks: Timber blocks are commonly used for framing and require a larger number compared to concrete or brick blocks.
Building Codes and Regulations, How many blocks can build 2 bedroom flat
Building codes and regulations are crucial in determining the block count. These codes specify minimum wall thicknesses, structural requirements, and other safety standards. They vary by location and are enforced to ensure the safety and stability of the structure. For example, some codes may require thicker walls for earthquake-prone areas, increasing the block count.
Building Design and Layout: How Many Blocks Can Build 2 Bedroom Flat

The configuration of a 2-bedroom flat significantly impacts the number of blocks required for its construction. Different floor plans and room arrangements influence the overall structure, affecting the amount of building material needed.
Impact of Floor Plans and Room Configurations
The arrangement of rooms and their dimensions directly influence the block count. For example, a flat with a large open-plan living area will require fewer internal walls compared to a flat with multiple smaller rooms. This translates to a lower block count for the open-plan design. Additionally, the number of doors and windows, their sizes, and the complexity of the building’s exterior also contribute to the block count.
Example Layout and Block Count Estimation
Consider a 2-bedroom flat with a typical layout:
- Living Room: 15 blocks for walls, 10 blocks for the floor, and 5 blocks for the ceiling.
- Kitchen: 10 blocks for walls, 5 blocks for the floor, and 3 blocks for the ceiling.
- Bedrooms (2): 12 blocks each for walls, 8 blocks each for the floor, and 4 blocks each for the ceiling.
- Bathroom: 8 blocks for walls, 4 blocks for the floor, and 3 blocks for the ceiling.
- Hallway: 5 blocks for walls, 3 blocks for the floor, and 2 blocks for the ceiling.
This example assumes a standard block size and does not account for additional features like built-in cabinets or decorative elements. The estimated total block count for this layout is approximately 120 blocks.
Block Count Comparison: Traditional vs. Open-Plan
A traditional layout with separate rooms typically requires more blocks for walls, doors, and windows compared to an open-plan design. For instance, a traditional 2-bedroom flat with a separate living room, dining area, and kitchen might require around 150 blocks, whereas an open-plan layout with a combined living-dining-kitchen area could require around 120 blocks. This difference is mainly due to the reduced number of internal walls in the open-plan design.
Practical Considerations and Estimation
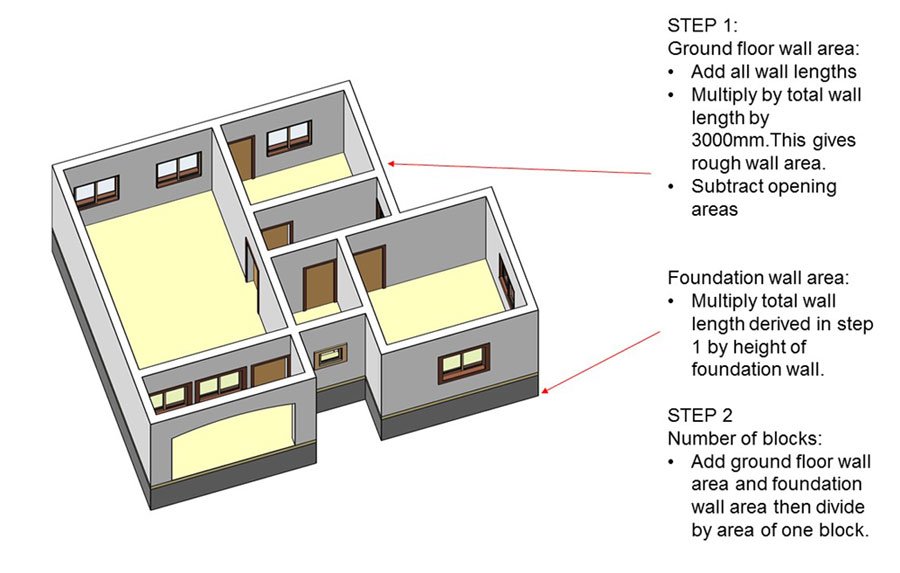
Estimating the number of blocks needed for a 2-bedroom flat requires careful consideration of various factors, including the building’s design, layout, and specific requirements. While the block count can be estimated based on blueprints and floor plans, several practical considerations can influence the final figure.
Estimating Block Count Based on Available Information
Estimating block count involves analyzing available information, such as blueprints, floor plans, and specifications. This information provides insights into the building’s dimensions, wall thicknesses, and other structural details. The process typically involves a combination of manual calculations and the use of online tools or calculators.
Step-by-Step Guide for Calculating Block Count
- Gather necessary information: This includes blueprints, floor plans, specifications, and any other relevant documents.
- Determine the building’s dimensions: Measure the length, width, and height of the flat, including walls, partitions, and any other structural elements.
- Calculate the total wall area: Multiply the length and height of each wall to determine the area. Add the areas of all walls to get the total wall area.
- Estimate the block size: Consider the standard block size used in your region. Standard block sizes can vary depending on local building codes and practices.
- Calculate the number of blocks per square meter: Divide the area of a single block by its length and width.
- Estimate the total block count: Divide the total wall area by the area of a single block. This gives an initial estimate of the total block count.
- Adjust for openings: Subtract the area of windows, doors, and other openings from the total wall area. This adjustment will provide a more accurate estimate of the block count.
- Factor in additional blocks: Account for blocks needed for columns, beams, and other structural elements. This can be estimated based on the building’s design and specifications.
- Add a safety margin: It’s recommended to add a 10-15% safety margin to account for potential waste, breakage, and unforeseen adjustments.
Using Online Tools or Calculators
Several online tools and calculators are available to assist in estimating block count. These tools typically require users to input the building’s dimensions, wall thicknesses, and other relevant information. The calculators then use algorithms to estimate the total block count.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Estimating block count can be challenging due to various factors, including:
- Complex building designs: Buildings with intricate layouts or unusual shapes can make accurate estimation difficult.
- Variations in block sizes: Standard block sizes can vary depending on the manufacturer and region.
- Unforeseen adjustments: Construction projects often require unforeseen adjustments, which can impact the final block count.
- Lack of detailed information: Incomplete or inaccurate blueprints and specifications can lead to inaccurate estimations.
It’s crucial to remember that these estimations are based on available information and can vary depending on actual construction requirements. Consult with a qualified builder or architect for a more accurate and comprehensive block count estimation.
